ORACLE
DATABASE:
è
Oracle is a Relational Database.
è
In Relational Database, All data is stored in
two dimensional tables that are composed of rows and columns.
è
Oracle Database enables us to store the data,
update it and efficiently retrive it.
è
Oracle provides a software to create and manage
the Oracle database.
è
The database consists of Physical and Logical
structures in which system, user and control information is stored.
è
Collectively, the software that runs the Oracle
and the Physical Database are called the Oracle
Database System.
ORACLE DB SERVER ARCHITECHTURE:
è
Oracle DB Server consists of two main components
as
·
Oracle Instance
·
Oracle Database
è
Oracle Instance has the two different sets of
components.
·
Background
Processes ( PMON, SMON, RECO, DBWn, LGWR, CKPT, ..etc. )
·
Memory Structures ( SGA, PGA )
è
Oracle Database inclues the two different structures
·
Logical structures ( Tablespaces, tables, views,
indexes, … etc. )
·
Physical structures ( control files, redolog files,
data files, parameter file,..etc.)
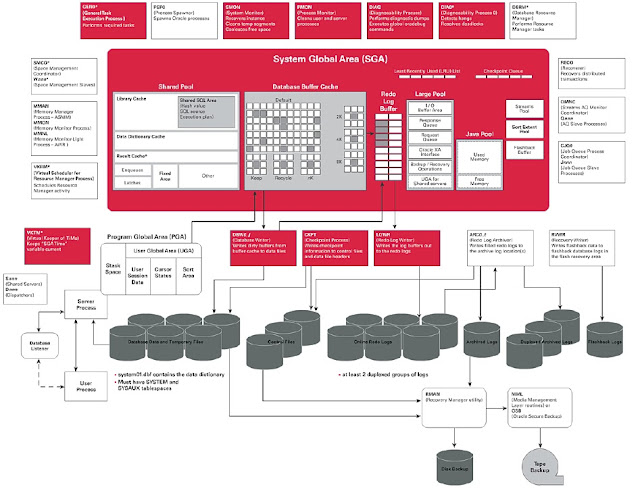
ORACLE DB SERVER ARCHITECHTURE DIAGRAM:
è
You will learn later in detail more about each
and every component operation structure
of the Oracle DB Server and structure of the Oracle Database where they are
relevent to the performance of specific database management tasks.
COMMON ORACLE DBA TASKS:
As an
Oracle DBA, you can expect to be involved in the following tasks:
- Installing Oracle software
- Creating Oracle databases
- Performing upgrades of the database
and software to new release levels
- Starting up and shutting down the
database
- Managing the database's storage
structures
- Managing users and security
- Managing schema objects, such as
tables, indexes, and views
- Making database backups and
performing recovery when necessary
- Proactively monitoring the
database's health and taking preventive or corrective action as required
- Monitoring and tuning performance
In a
small to midsize database environment, you might be the sole person performing
these tasks. In large, enterprise environments, the job is often divided among
several DBAs, each with their own area of specialty, such as the database
security administrator or database tuning expert.
TOOLS FOR ADMINISTERING THE DATABASE:
The
intent of this book is to allow you to quickly and efficiently create an Oracle
database, and to provide guidance in basic database administration.
The
following are some of the products, tools, and utilities you can use in
achieving your goals as a database administrator.
- Oracle Universal Installer (OUI)
The
Oracle Universal Installer installs your Oracle software and options. It can
automatically launch the Database Configuration Assistant to install a
database.
- Database Configuration Assistant
(DBCA)
The
Database Configuration Assistant creates a database from templates that are
Oracle supplied, or you can create your own. It enables you to copy a
preconfigured seed database, thus saving the time and effort of customizing and
generating a database from scratch.
- Database Upgrade Assistant
This
tools guides you through the upgrade of your existing database to a new Oracle
release.
- Oracle Net Manager
This
tool guides you through your Oracle Net network configuration.
- Oracle Enterprise Manager
The
primary tool for managing your database is Oracle Enterprise Manager, a
web-based interface. After you have installed the Oracle software, created or
upgraded a database, and configured the network, you can use Oracle Enterprise
Manager as the single interface for managing your database. In addition, Oracle
Enterprise Manager also provides an interface for performance advisors and an
interface for Oracle utilities such as SQL*Loader and Recovery Manager.
No comments:
Post a Comment